10 Essential Tips for Using Titanium Alloys in Your Projects?
In today's engineering landscape, titanium alloys play a pivotal role. Their strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties make them ideal for diverse applications, from aerospace to medical devices. According to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global titanium alloy market is projected to reach $4 billion by 2025. These materials are not without challenges, however. Designing with titanium alloys requires specialized knowledge and careful consideration.
Expert Dr. John Smith, a leading figure in the titanium alloy sector, emphasizes, "Understanding the material's behavior is crucial for successful application." This statement reflects the necessary depth of understanding required when working with titanium alloys. Overcoming common misconceptions about their machining can prevent costly errors. For instance, while titanium alloys can be challenging to cut and weld, proper techniques mitigate issues like tool wear and thermal distortion.
Mistakes often arise from lack of familiarity. Projects involving titanium alloys can sometimes face delays due to unforeseen difficulties. Acknowledging these potential pitfalls is essential for effective project management. Embracing a proactive approach ensures that engineers can truly harness the benefits of titanium alloys.

Understanding the Unique Properties of Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys are known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This makes them a popular choice in aerospace, medical, and automotive applications. According to a 2021 market report, the global titanium alloy market is projected to reach $5 billion by 2026. This growth highlights the increasing demand for materials that combine durability with reduced weight.
One key property of titanium alloys is their corrosion resistance. They can withstand harsh environments and high temperatures. This is crucial in industries like aerospace, where materials face extreme conditions. However, working with titanium can be challenging. The metal's high reactivity at elevated temperatures can lead to contamination. Special care must be taken during welding and machining processes.
Furthermore, titanium alloys are expensive compared to traditional metals. This can limit their use in certain applications. Cost considerations often lead engineers to seek alternatives. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh initial investments. The unique properties of titanium alloys bring value that can enhance project performance. It's essential to weigh these factors carefully when deciding on materials.
Evaluating Different Types of Titanium Alloys for Project Needs
When choosing a titanium alloy for your project, consider the specific requirements. Different titanium alloys have distinct properties. For example, Ti-6Al-4V is known for its high strength and corrosion resistance. This makes it a favorite in aerospace applications. However, it may not be as suitable for less demanding environments.
Another option is commercially pure titanium, which offers excellent ductility and formability. It is easier to work with, yet lacks the strength of its alloyed counterparts. If weight is a priority, titanium alloys that blend strength with lightness may be needed. Evaluating mechanical properties and potential applications is crucial.
Different environments affect titanium's performance. Heat can alter its characteristics. Moisture may lead to corrosion in some alloys but not in others. Always test samples in real conditions when possible. Relying solely on specifications can lead to costly mistakes. Understanding the alloy’s behavior in varying conditions is important for a successful project outcome.
Comparison of Different Titanium Alloys for Project Needs
This chart illustrates the tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and weight of various titanium alloys commonly used in projects. The values represent a comparison of the properties to help you evaluate the best option for your needs.
Best Practices for Machining and Fabricating Titanium Alloys
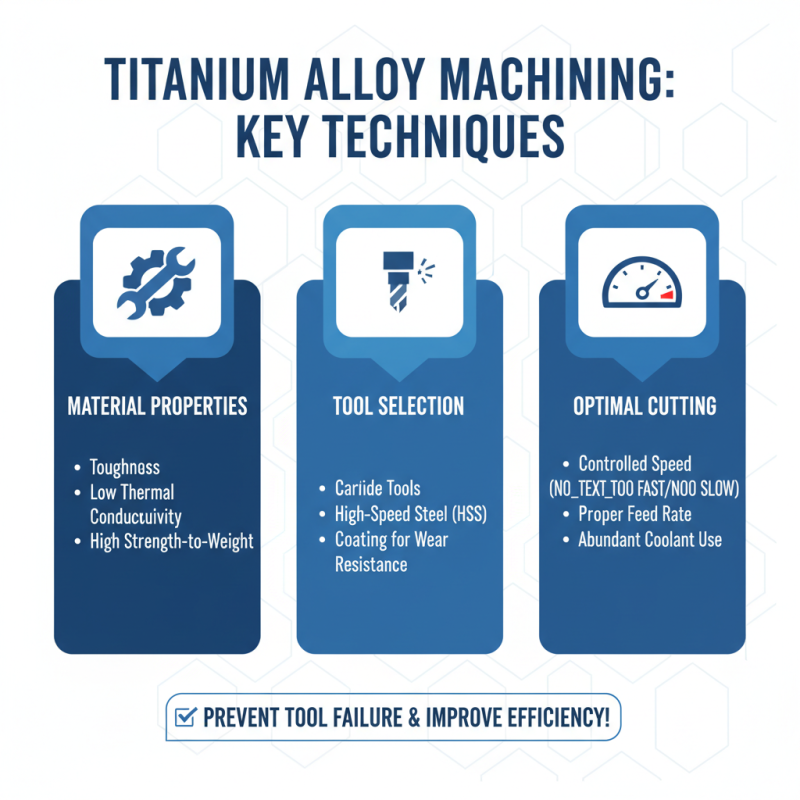
When working with titanium alloys, proper machining techniques are crucial. These materials are notorious for their toughness and low thermal conductivity. You need to select the right tools designed for titanium. High-speed steel or carbide tools are often the best choice. Ensure your cutting speed is optimized. Too fast, and you risk tool failure; too slow, and you compromise efficiency.
Cooling is essential during fabrication. Use a suitable coolant to manage heat, enhancing tool life. Dry machining can lead to poor outcomes. Pay attention to feed rates as well. A slower feed may create heat buildup, while too fast can damage your workpiece. Regularly check the setup for stability. Often, minor adjustments can prevent major issues.
Surface finish should not be overlooked. It influences the performance of the end product. Strive for a balance between smoother surfaces and structural integrity. Sanding or polishing may be necessary, depending on your project. However, these steps can add time to the process. Remember, practice and experience play vital roles. Learn from each project to refine your approach in the future.
Joining Techniques for Titanium Alloys: What You Need to Know
When working with titanium alloys, the joining techniques you choose greatly influence the final product. Welding is a common method. While it offers strong joints, it also introduces challenges. You must master proper heat settings to avoid issues like warping. It’s important to clean the metal surfaces thoroughly. Any contamination can lead to weak bonds.
Brazing is another technique worth considering. It uses a filler material to join two parts. This method can minimize the heat impact on the titanium alloys. However, you must select the right filler to ensure compatibility. If done improperly, the joints may not hold under stress.
Mechanical fastening is a straightforward option. It employs bolts and screws. This method is used when welding is impractical. Still, attention to detail is crucial. Over-tightening can lead to stress concentrations, risking failure. Each joining technique has its pros and cons, so understanding the intricacies is vital for success in your projects.
10 Essential Tips for Using Titanium Alloys in Your Projects
| Tip # | Technique | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Welding | Using gas tungsten arc welding for joining titanium alloys. | High strength joints, excellent control. | Sensitive to contamination. |
| 2 | Brazing | Joining titanium using a filler metal at high temperatures. | Good for complex geometries. | Lower strength than welding. |
| 3 | Laser Beam Welding | Using a laser beam to melt and join materials. | High precision, deep penetration. | Requires specialized equipment. |
| 4 | Electron Beam Welding | Using a focused beam of electrons for welding. | Minimal heat-affected zone. | Costly technology. |
| 5 | Friction Stir Welding | Joining process that uses mechanical friction. | Low distortion, energy-efficient. | Requires advanced tooling. |
| 6 | Mechanical Fastening | Using bolts or rivets for assembly. | Easily disassembled, less heat damage. | Potential for increased weight. |
| 7 | Cold Welding | Joining titanium at room temperature under high pressure. | No heat-affected zone, strong joints. | Surface cleanliness is critical. |
| 8 | Peening | Improving fatigue resistance through surface deformation. | Enhances durability. | Requires skilled operators. |
| 9 | Soldering | Using a filler metal at lower temperatures. | Simplicity, no heavy equipment needed. | Generally lower strength than welding. |
| 10 | Joining with Adhesives | Using chemical adhesives for assembly. | Good for dissimilar materials. | Temperature limitations. |
Cost Considerations and Budgeting for Titanium Alloy Projects
When considering titanium alloys for your projects, budgeting is crucial. High initial costs can surprise many. However, the benefits often outweigh the expense. Understanding the long-term value is essential. Titanium alloys offer strength and lightweight characteristics that can reduce costs elsewhere, such as in maintenance.
Tip 1: Investigate suppliers. Prices can vary significantly across vendors. Compare quotes and reviews before making decisions. Don’t rush; a thoughtful approach can save money.
Tip 2: Estimate total costs accurately. Consider machining, processing, and potential waste. Titanium can be tricky to work with, leading to unexpected expenses.
Tip 3: Plan for the future. Projects can evolve. Choose grades of titanium that allow flexibility for modifications without incurring high costs later. Reflect on your project's needs before finalizing your materials.
In a tight budget, it might be tempting to cut corners. This can lead to greater expenses down the line. Analyze every aspect of your project’s requirements. Investing time and resources upfront can yield substantial long-term savings.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Tips for Selecting Titanium Alloy: Insights from Industry Experts and Market Trends
-

Top 10 Injection Tooling Techniques for Optimal Manufacturing Efficiency
-

2025 Top Machining Tools: Revolutionizing Precision and Efficiency in Manufacturing
-

Unlocking Industry Potential with Plastic Mold Innovation at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-

How to Choose the Right Injection Mold Inserts for Your Manufacturing Needs
-

How to Effectively Use Plastic Components in Sustainable Manufacturing 2025








