What is Plastic Injection Mold? A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Plastic injection molding is a revolutionary manufacturing process that has transformed the landscape of industrial production. According to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global plastic injection molding market size was valued at approximately $249.9 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% from 2022 to 2030. This remarkable growth is driven by the surging demand for lightweight and durable plastic components across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
As noted by industry expert Dr. Emily Chen, "The precision and efficiency of plastic injection molding make it indispensable in modern manufacturing. Its ability to produce complex shapes with impeccable repeatability significantly reduces production time and costs." This statement underlines the importance of understanding the intricacies of the plastic injection mold process for professionals entering this field.
In this comprehensive guide for beginners, we will explore the fundamentals of plastic injection molds, including their design and operational aspects, while also highlighting the factors influencing their performance and longevity. With this foundational knowledge, readers will be better equipped to appreciate the significant role that plastic injection molding plays in contemporary manufacturing processes.
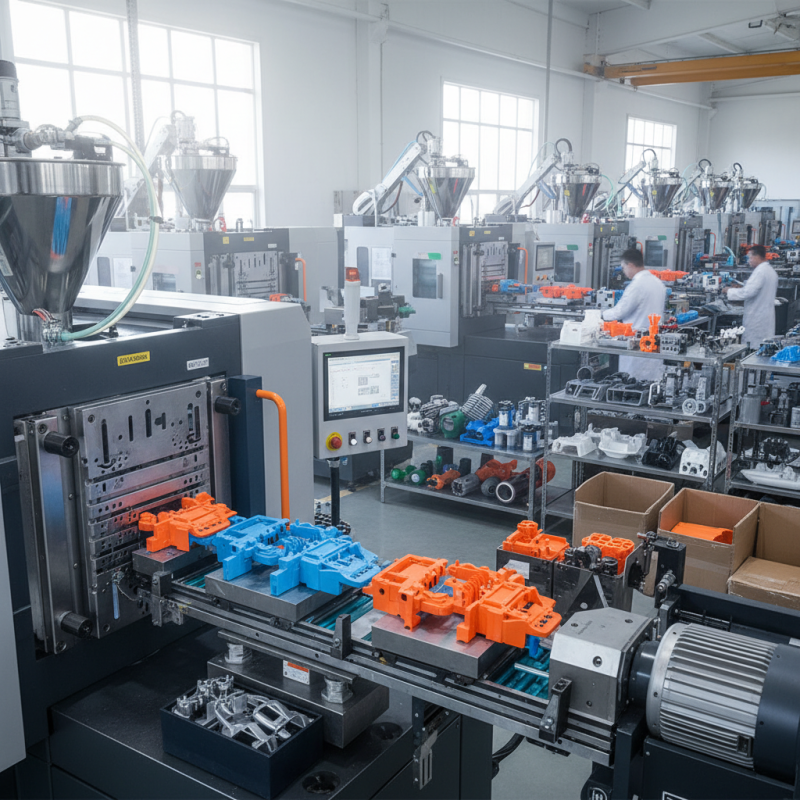

Definition and Overview of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold. This technique is highly efficient and is widely utilized in various industries due to its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision. The process begins with the creation of a mold, which is typically made from steel or aluminum, designed to the specifications of the desired part. Once the mold is ready, plastic pellets are heated until they melt and then injected under pressure into the mold cavity. After the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected.
One of the key advantages of plastic injection molding is its scalability. It allows for the mass production of plastic components, making it cost-effective for large production runs. The process also minimizes waste, as excess plastic can often be recycled and reused. Additionally, injection molding supports a wide range of plastic materials, enabling manufacturers to select the best type of plastic for their specific application, whether for strength, flexibility, or durability. The versatility of injection molding makes it an essential technique in producing everything from small components to large industrial parts.
Key Components of Plastic Injection Molds Explained
Plastic injection molds are intricate tools that play a crucial role in the manufacturing process of plastic products. Understanding the key components of these molds is essential for anyone looking to delve into the world of plastic molding. The primary components of an injection mold include the mold base, mold cavity, and ejector system.
The mold base serves as the backbone, providing the structure and support needed to hold all other elements together. It consists of two halves, the core and the cavity, which come together to form the shape of the desired plastic part. The mold cavity is the hollow shape carved out of the mold that gives the final product its form. This component can be custom designed for a wide variety of shapes and sizes, tailored to the specific needs of the product being manufactured.
Another vital aspect is the ejector system, which is designed to remove the finished product from the mold once the plastic has cooled and solidified. The ejector pins push the product out, ensuring that it does not adhere to the cavity walls. Together, these components function harmoniously during the injection molding process, allowing for efficient production and precise shaping of plastic items across various industries.
The Plastic Injection Molding Process Step-by-Step

The plastic injection molding process is a highly efficient manufacturing technique used to produce parts in large quantities. It begins with the creation of a mold, which is typically made from metal and designed to the specific shape and dimensions of the desired part. The process commences with heating plastic granules until they become molten. Once at the right temperature, this liquid plastic is injected into the mold under high pressure. This crucial step ensures that the material fills every cavity and detail of the mold, resulting in high precision.
After the plastic has been injected, it is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold. Cooling time varies depending on the size and complexity of the part, but it is essential for achieving the desired strength and quality. Once the cooling process is complete, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. This step may involve the use of ejector pins to ensure that the part is released without damage. Finally, any excess material or imperfections may be trimmed, and the parts are then ready for further processing or assembly, making the plastic injection molding process swift and efficient for producing high-quality plastic components.
Applications and Industries Utilizing Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that finds applications across a wide range of industries. It involves injecting molten plastic into molds to create intricate shapes and designs. This method is particularly popular in sectors such as automotive, consumer goods, packaging, electronics, and medical devices. The automotive industry, for instance, utilizes plastic injection molding for producing components like dashboards, bumpers, and interior fixtures, where lightweight and durable materials are essential for enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Moreover, the consumer goods sector benefits greatly from this molding technique, as it allows for the mass production of everyday items like containers, toys, and household appliances. The precision and efficiency of plastic injection molding enable manufacturers to produce complex geometries at lower costs, meeting the demands of an ever-evolving market. Additionally, in the medical field, customized plastic parts for devices such as syringes, tubes, and surgical instruments are produced with high accuracy and sterility, addressing safety and functionality requirements critical in healthcare applications. This highlights the significant role of plastic injection molding in driving innovation and efficiency across diverse industries.
What is Plastic Injection Mold? A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners - Applications and Industries Utilizing Plastic Injection Molding
| Application | Industry | Materials Used | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Parts | Automotive | ABS, Polycarbonate | High precision, rapid production |
| Consumer Electronics | Electronics | Polypropylene, Nylon | Complex designs, ideal for high volumes |
| Medical Devices | Healthcare | Polyethylene, Polystyrene | Sterile, durable components |
| Household Goods | Consumer Goods | Polypropylene, PVC | Cost-effective, lightweight products |
| Packaging Solutions | Packaging | PET, HDPE | Versatile, high-volume production |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastic Injection Molding Techniques
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that offers several advantages. One of the primary benefits is its ability to produce complex shapes and designs with high precision and consistency. This makes it ideal for mass production, as molds can be created to replicate the same dimensions repeatedly, reducing waste and ensuring product uniformity. Additionally, the process can accommodate a variety of materials, allowing for versatility in production, whether for consumer goods, automotive parts, or medical devices.
However, there are also disadvantages to consider. The initial cost of creating molds can be quite high, which may not be cost-effective for small production runs. Additionally, the design and manufacturing of molds require significant lead time, making the process less flexible when it comes to changes in design or quick responses to market demands. Moreover, the extensive use of plastics raises environmental concerns, as improper disposal can lead to long-lasting waste issues. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for businesses considering plastic injection molding as a viable production method.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastic Injection Molding
Related Posts
-
Exploring Innovations in Plastic Injection Molds at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Unlocking Industry Potential with Plastic Mold Innovation at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-
Understanding the Role of Plastic Injection Molds in Modern Manufacturing Processes
-

Exploring Innovation: How Plastic Industries are Shaping Sustainable Technology for the Future
-

Understanding the Process and Advantages of Plastic Injection Molded Parts in Modern Manufacturing
-

How to Achieve Superior Results with Super Finishing Techniques








