What Types of Manufacturing Applications Are Transforming Industry Today?
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the integration of advanced manufacturing applications that enhance productivity, efficiency, and innovation. According to a report by Deloitte, the adoption of automation and digital technologies in manufacturing can lead to productivity increases of up to 30% within just five years. These advancements are not only reshaping production processes but also redefining supply chain management, operational protocols, and quality assurance standards across various industries.
In recent years, the rise of Industry 4.0 has propelled the development of smart manufacturing applications, incorporating technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), artificial intelligence, and machine learning. McKinsey’s insights reveal that manufacturing companies implementing these technologies can expect a 20-30% improvement in overall equipment effectiveness. With real-time data analytics and predictive maintenance, manufacturers can minimize downtime and optimize resource allocation, ultimately boosting profitability.
As we delve deeper into the transformative manufacturing applications currently shaping the industry, it is crucial to recognize the pivotal role of these technologies in fostering sustainable growth and competitive advantage. This exploration will highlight the specific applications that are leading the charge, showcasing their impact on diverse sectors and the future trajectory of manufacturing as a whole.

Types of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies Transforming Industry Today

Advanced manufacturing technologies are revolutionizing the industrial landscape by integrating cutting-edge innovations into traditional manufacturing processes. One of the most significant advancements is the use of automation and robotics. These technologies not only enhance efficiency and precision but also reduce the dependency on human labor for repetitive tasks. As collaborative robots or cobots become more prevalent, they are designed to work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity while maintaining safety.
Another transformative technology is additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing. This method allows for the rapid prototyping and production of complex parts with minimal material waste, leading to more sustainable manufacturing practices. Industries ranging from aerospace to healthcare are leveraging 3D printing to create customized components that meet specific complex requirements, thus shortening lead times and enabling more flexible supply chains. Furthermore, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices into manufacturing plants has begun to create smart factories. These interconnected machines communicate in real-time, providing manufacturers with valuable data insights that drive predictive maintenance and optimize operational efficiency.
The convergence of these advanced technologies is reshaping the future of manufacturing, leading to smarter, faster, and more sustainable practices that are essential for remaining competitive in today's ever-evolving market. By harnessing these innovations, industries can adapt to changing consumer demands and improve overall productivity.
Impact of Automation and Robotics on Manufacturing Efficiency and Productivity
The integration of automation and robotics in manufacturing is reshaping the industry landscape and significantly enhancing efficiency and productivity. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, implementing automation solutions can increase overall productivity by up to 30% in certain manufacturing processes. Automation not only streamlines operations but also reduces human error, leading to improved quality and consistency in production lines.
Furthermore, the rise of advanced robotics has enabled manufacturers to adopt flexible production methods. A study by the International Federation of Robotics indicates that global sales of industrial robots have surged, with a growth rate of 12% annually. This surge is reflective of the industry’s shift towards more automated systems, which help to meet the growing consumer demand for faster turnaround times and customization. With robots capable of operating 24/7, manufacturers are seeing significant reductions in downtime and an overall increase in throughput, positioning them to respond swiftly to market changes.
The implementation of these technologies also extends to data analytics, which offers manufacturers valuable insights into operational performance. By harnessing real-time data, companies can identify bottlenecks and optimize processes for better efficiency. According to a report by Deloitte, manufacturers that leverage advanced analytics are three times more likely to improve their operational performance significantly compared to their peers. These advancements are not just reshaping how products are made; they are redefining the entire manufacturing paradigm.
Impact of Automation and Robotics on Manufacturing Efficiency and Productivity
Role of Additive Manufacturing in Reducing Production Costs and Lead Times
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape by significantly reducing production costs and lead times. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which often require extensive material and energy, additive manufacturing builds components layer by layer. This efficiency not only minimizes waste but also allows for the rapid prototyping of complex designs, enabling manufacturers to iterate quickly and adapt to market demands. The ability to create highly customized products without the need for extensive tooling has led to a streamlined production process, reducing overhead costs associated with inventory and storage.
Furthermore, additive manufacturing is playing a critical role in supply chain optimization. By enabling localized production, manufacturers can reduce transportation costs and time, resulting in a more resilient and responsive supply chain. For sectors such as aerospace and healthcare, where precision and speed are paramount, the benefits of additive manufacturing are particularly pronounced. Parts can be produced on demand, significantly shortening lead times and ensuring that businesses can maintain competitive advantage in an ever-evolving market. As the technology continues to advance, its impact on reducing costs and enhancing efficiency across various manufacturing applications is likely to grow, shaping the future of the industry.
What Types of Manufacturing Applications Are Transforming Industry Today? - Role of Additive Manufacturing in Reducing Production Costs and Lead Times
| Application Type | Description | Cost Reduction (%) | Lead Time Reduction (%) | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Additive manufacturing process that builds objects layer by layer. | 25 | 50 | High |
| Rapid Prototyping | Quickly creating a scale model of a physical part or assembly. | 30 | 60 | Medium |
| Custom Tooling | Creating specialized tools using additive processes to suit specific tasks. | 20 | 40 | High |
| Spare Parts Production | On-demand production of spare parts to reduce inventory costs. | 15 | 30 | High |
| Mass Customization | Producing personalized products at scale using additive technologies. | 35 | 70 | High |
Integration of IoT and Smart Manufacturing for Real-Time Data Analysis
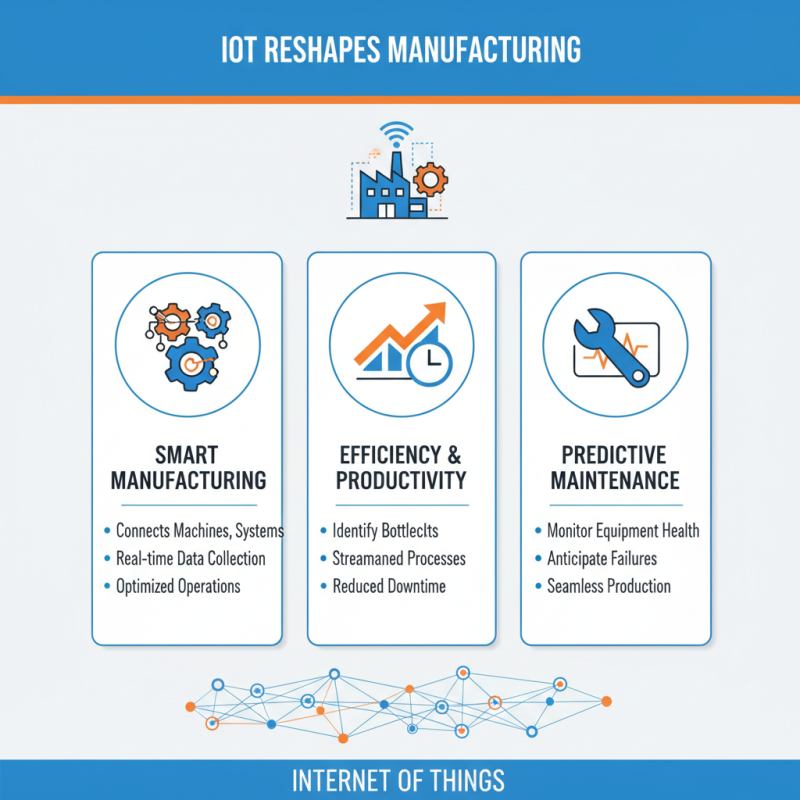
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into manufacturing processes is reshaping the industry by enabling smart manufacturing practices that drive efficiency and productivity. By connecting machines, sensors, and systems through IoT technology, manufacturers can collect vast amounts of real-time data from the production floor. This data is invaluable for identifying bottlenecks and optimizing operations, leading to more streamlined processes and reduced downtime. With the ability to monitor equipment health and performance remotely, manufacturers can also anticipate maintenance needs, thereby minimizing unexpected failures and ensuring seamless production.
Moreover, real-time data analysis provides manufacturers with deeper insights into their supply chains, allowing for better decision-making and resource allocation. Advanced analytics tools can process this data, generating actionable insights that help in forecasting demand, managing inventory, and refining product quality. As a result, the shift towards an interconnected manufacturing environment not only enhances operational agility but also fosters innovation, enabling companies to adapt quickly to market changes and consumer preferences. This transformative approach is a pivotal aspect of modern manufacturing that is setting the stage for future industry advancements.
Sustainability Practices in Manufacturing: Innovations and Industry Statistics
Sustainability practices in manufacturing are rapidly evolving, driven by a growing awareness of environmental impact and the necessity for efficient resource management. A recent report from the World Economic Forum highlights that 67% of manufacturers now prioritize sustainability as a core component of their business strategy. This shift not only addresses regulatory pressures but also meets the increasing demand for eco-friendly products. Innovations such as circular manufacturing and renewable energy integration are reshaping traditional production processes, allowing companies to minimize waste and reduce emissions significantly.
Implementing sustainable practices can also lead to substantial cost savings. According to a study by McKinsey & Company, organizations that adopt circular economy principles see a 30% reduction in production costs over five years. Experts suggest that manufacturers consider investing in energy-efficient technologies and supply chain transparency to further enhance their sustainability efforts.
Tips: To effectively integrate sustainability into your manufacturing operations, start by conducting a sustainability audit to identify areas for improvement. Utilize data analytics to track energy usage and waste production trends, enabling you to make informed decisions. Collaborating with suppliers who share your sustainability goals can also amplify the impact of your efforts, making it easier to implement greener practices throughout the entire supply chain.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Additive Manufacturing Innovations at the 2025 Canton Fair in China
-

Transforming Industries: Unleashing the Power of Cutting-Edge Industrial Applications
-

10 Essential Tips for Selecting Titanium Alloy: Insights from Industry Experts and Market Trends
-

How to Achieve Superior Results with Super Finishing Techniques
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Impact of Super Finishing Process on Product Quality and Efficiency
-
Why is Surface Finishing Process Essential for Product Quality?








